PFMI 1: Legal basis
A CCP should have a well-founded, clear, transparent, and enforceable legal basis for each material aspect of its activities in all relevant jurisdictions.
View Demo
A CCP should have a well-founded, clear, transparent, and enforceable legal basis for each material aspect of its activities in all relevant jurisdictions.
View Demo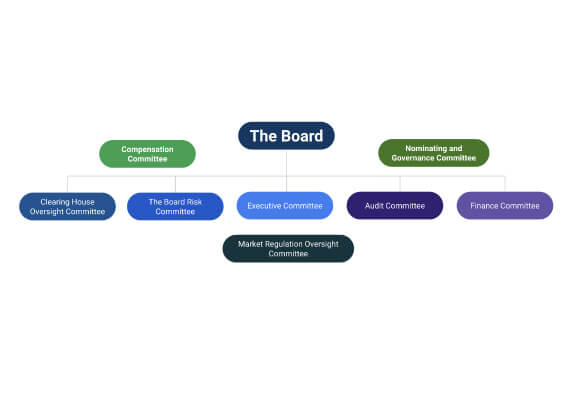
A CCP should have governance arrangements that are clear and transparent, promote the safety and efficiency of the CCP, and support the stability of the broader financial system, other relevant public interest considerations, and the objectives of relevant stakeholders.
View Demo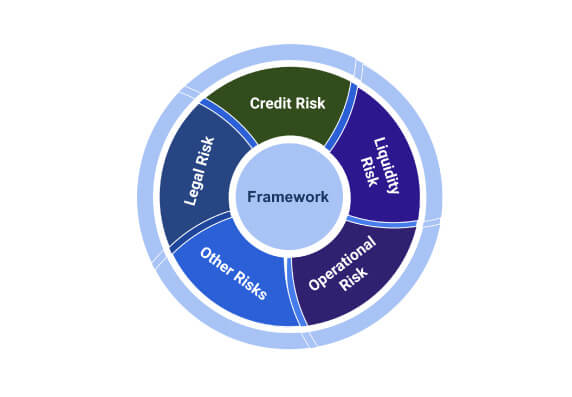
A CCP should have a sound risk-management framework for comprehensively managing legal, credit, liquidity, operational, and other risks.
View Demo
A CCP should measure, monitor, and manage its credit exposures to CPs and intermediaries & maintain sufficient resources to cover exposure to each or the two largest CPs with a high degree of confidence.
View Demo
A CCP that requires collateral to manage its or CP’s credit exposure should accept collateral with low credit, liquidity, and market risks. A CCP should also set and enforce appropriately conservative haircuts and concentration limits.
View Demo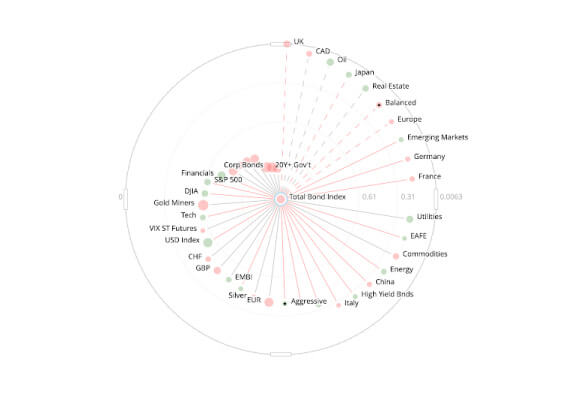
A CCP should cover its credit exposures to its participants for all products through an effective margin system that is risk-based and regularly reviewed.
View Demo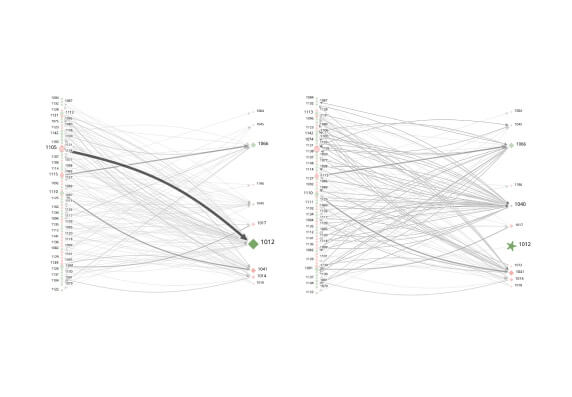
A CCP should measure, monitor, and manage its liquidity risk; maintain liquidity across currencies for same-day and, where appropriate, intraday and multi day settlement of obligations under a wide range of extreme but plausible market conditions.
View Demo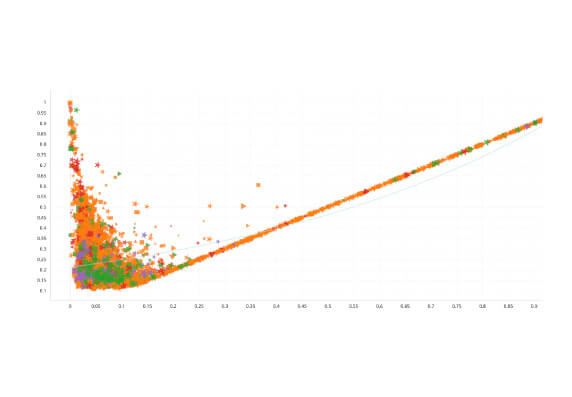
A CCP should provide clear and certain final settlement, at a minimum by the end of the value date. Where necessary or preferable, a CCP should provide final settlement intraday or in real time.
View Demo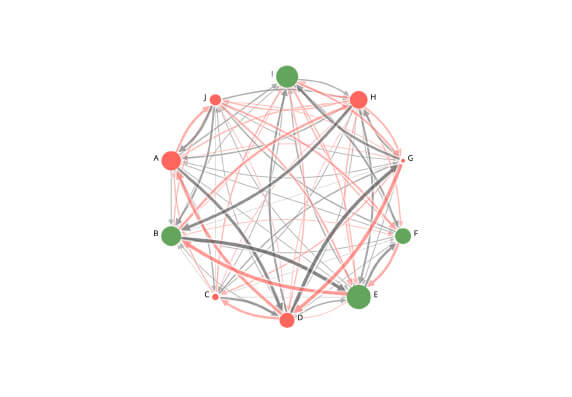
A CCP should conduct its money settlements in central bank money where practical and available. If central bank money is not used, a CCP should minimise and strictly control the credit and liquidity risk arising from the use of commercial bank money.
View Demo
A CCP should clearly state its obligations with respect to the delivery of physical instruments or commodities and should identify, monitor, and manage the risks associated with such physical deliveries.
View Demo
A CSD should have appropriate rules and procedures to help ensure the integrity of securities issues and minimise and manage the risks associated with the safekeeping and transfer of securities. A CSD should maintain securities in an immobilised or dematerialised form for their transfer by book entry.
View Demo
If an FMI settles transactions that involve the settlement of two linked obligations (e.g. securities or FX transactions), it should eliminate principal risk by conditioning the final settlement of one obligation upon the final settlement of the other.
View Demo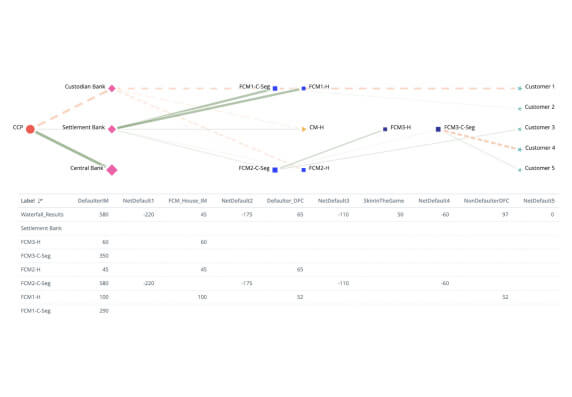
A CCP should have effective and clearly defined rules and procedures to manage a participant default. These rules and procedures should be designed to ensure that the CCP can take timely action to contain losses and liquidity pressures and continue to meet its obligations.
View Demo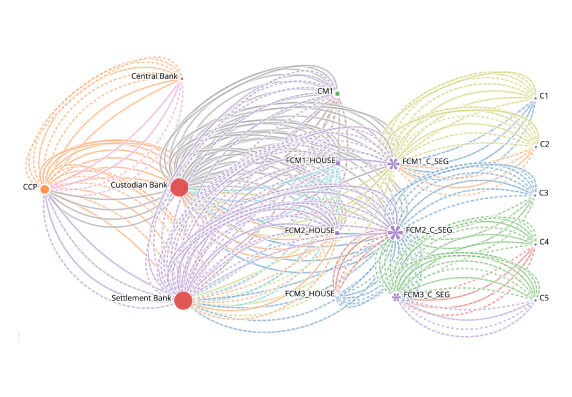
A CCP should have rules and procedures that enable the segregation and portability of positions of a participant’s customers and the collateral provided to the CCP with respect to those positions.
View Demo
A CCP should identify, monitor, and manage its general business risk and hold liquid net assets funded by equity to ensure a recovery or orderly wind-down of critical operations and services.
View Demo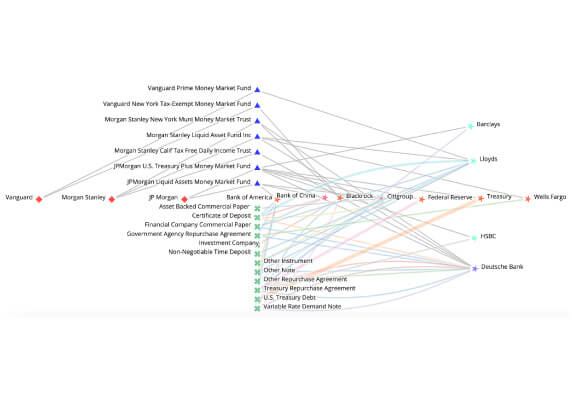
A CCP should safeguard its own and its participants’ assets and minimise the risk of loss on and delay in access to these assets. A CCP’s investments should be in instruments with minimal credit, market, and liquidity risks.
View Demo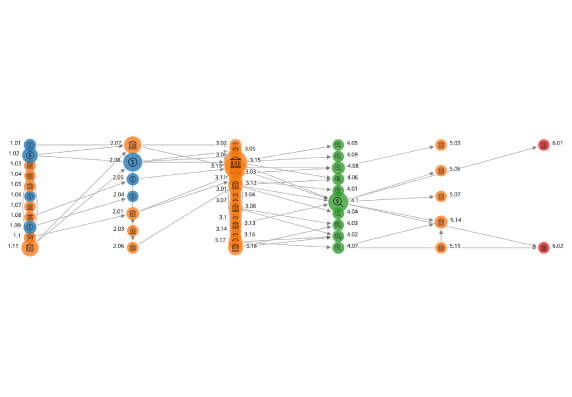
A CCP should identify the plausible sources of operational risk and mitigate their impact through the use of appropriate systems, policies, procedures, and controls. Systems should be designed to ensure a high degree of security and operational reliability and should have adequate, scalable capacity. Business continuity management should aim for timely recovery of operations and fulfilment of the CCP’s obligations, including in the event of a wide-scale or major disruption.
View Demo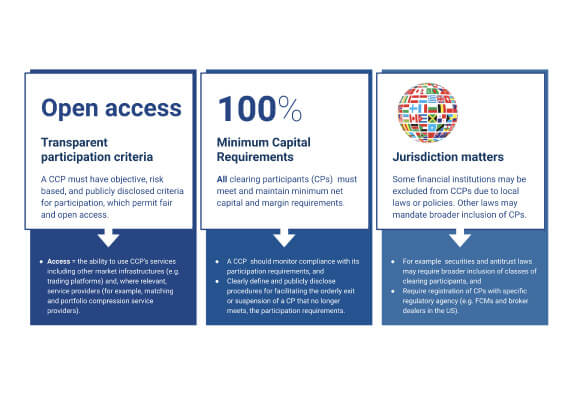
A CCP should have objective, risk-based, and publicly disclosed criteria for participation, which permit fair and open access.
View Demo
A CCP should identify, monitor, and manage the material risks to the CCP arising from tiered participation arrangements.
View Demo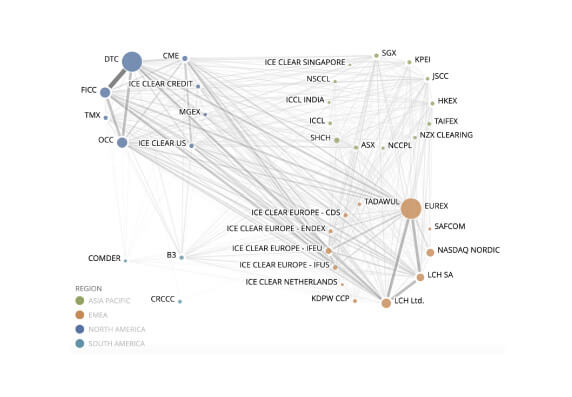
A CCP that establishes a link with one or more CCPs should identify, monitor, and manage link-related risks.
View Demo
A CCP should be efficient and effective in meeting the requirements of its participants and the markets it serves.
View Demo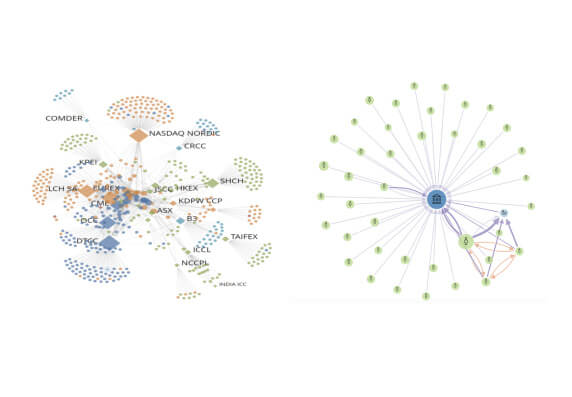
A CCP should use, or at a minimum accommodate, relevant internationally accepted communication procedures and standards in order to facilitate efficient payment, clearing, settlement, and recording.
View Demo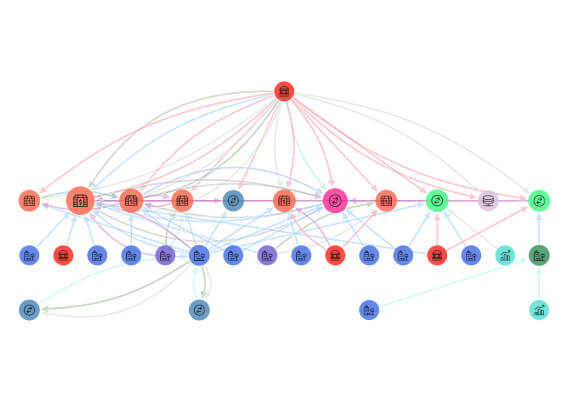
A CCP must have clear, comprehensive, and publicly disclosed rules/procedures for CPs to have an accurate understanding of the risks, fees, and other material costs.
View Demo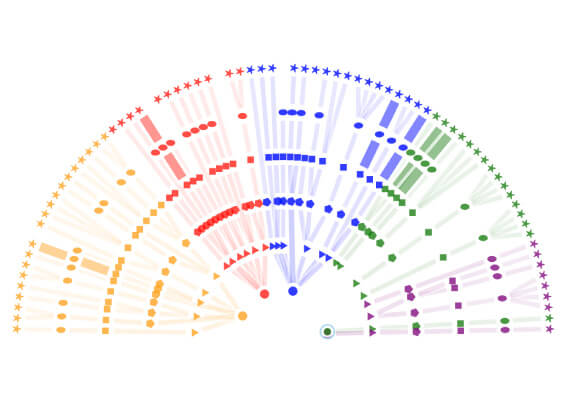
A TR should provide timely and accurate data to relevant authorities and the public in line with their respective needs.
View Demo